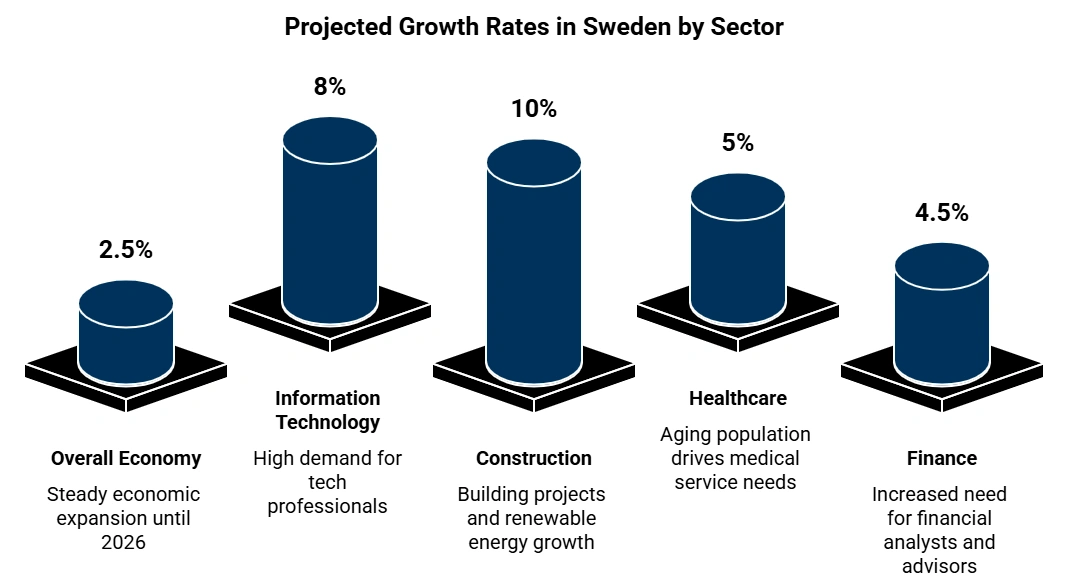
Sweden presents opportunities for UK professionals seeking employment in its rapidly growing sectors. With its emphasis on innovation, technology, and sustainable practices, Sweden's economy shows consistent strength. There is an increasing demand for experts in healthcare, information technology, construction, and finance. Swedish work visa holders often find attractive salaries, a high standard of living, and a favorable work-life balance.
*Want assistance to apply for Sweden Work Visa? Y-Axis is here to assist with the process.
Sweden provides workers a supportive work setting with fair wages, tax benefits, and quality healthcare. Its populace enjoys a work-life balance due to paid leave and a safe society. Sweden values innovation and environmental protection, making it a worthwhile place for career advancement. With people from diverse backgrounds, most workers can feel at home there.
Sweden is currently facing skills shortages across multiple sectors, driven by an ageing population, digital transformation, and demand for sustainable infrastructure. The Public Employment Service (Arbetsförmedlingen) and Statistics Sweden report over 180 occupations experiencing workforce gaps, especially in healthcare, education, ICT, and skilled trades.
| Sector | In-Demand Roles |
| Healthcare | Registered Nurses, Specialist Doctors, Midwives, Physiotherapists, Psychologists |
| IT & Digital Tech | Software Developers, System Analysts, IT Architects, Network Engineers |
| Engineering & Trades | Civil, Electrical, Chemical Engineers; Plumbers, Electricians, Machine Operators |
| Education | Preschool Teachers, Secondary Educators, Vocational Trainers, Special Needs Teachers |
| Logistics & Transportation | Truck Drivers, Bus/Tram Operators, Freight Coordinators, Transport Planners |
| Hospitality & Services | Bakers, Chefs, Laboratory Technicians, Care Assistants, Security Guards |
Given below is a detailed overview of the High-Demand Occupations by sector:
Sweden's health care industry is experiencing rapid growth driven by an aging population, which is creating increased need for physicians, nurses, and allied health staff. With considerable public investment directed toward health care infrastructure and systems, health care professionals are required to follow rigorous standards and protocols.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Specialist Doctor | 700,000 – 1,200,000 |
| General Practitioner | 500,000 – 800,000 |
| Registered Nurse | 350,000 – 550,000 |
| Pharmacist | 500,000 – 700,000 |
| Physiotherapist | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Medical Laboratory Technician | 300,000 – 500,000 |
| Radiologist | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Aged Care Worker | 250,000 – 400,000 |
| Healthcare Manager | 800,000 – 1,200,000 |
| Clinical Psychologist | 500,000 – 750,000 |
Sweden's information technology sector is seeing constant growth and innovation. Because of Sweden's focus on digitization and smart city creation, there is an increasing demand for software developers, cybersecurity experts, and data scientists.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Software Developer | 500,000 – 700,000 |
| Data Scientist | 600,000 – 800,000 |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | 600,000 – 1,000,000 |
| IT Project Manager | 700,000 – 1,100,000 |
| Cloud Engineer | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Network Administrator | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Systems Analyst | 500,000 – 800,000 |
| IT Consultant | 600,000 – 950,000 |
| DevOps Engineer | 600,000 – 850,000 |
| Web Developer | 450,000 – 700,000 |
Sweden is well-known for its engineering achievements, which include both renewable energy and better infrastructure. The country's focus on lasting growth means there is a high demand for civil, mechanical, and electrical engineers.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Civil Engineer | 500,000 – 700,000 |
| Mechanical Engineer | 550,000 – 800,000 |
| Electrical Engineer | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Renewable Energy Engineer | 700,000 – 1,000,000 |
| Project Manager (Engineering) | 800,000 – 1,200,000 |
| Structural Engineer | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Environmental Engineer | 500,000 – 800,000 |
| Petroleum Engineer | 900,000 – 1,200,000 |
| Aerospace Engineer | 700,000 – 1,000,000 |
| Engineering Manager | 1,000,000 – 1,500,000 |
The expansion of Sweden’s financial services sector is creating increased demand for professionals in fields such as accounting, investment banking, and tax advising. Economic growth in Sweden is expected to further fuel this demand.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Financial Analyst | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Chartered Accountant | 600,000 – 800,000 |
| Tax Consultant | 500,000 – 750,000 |
| Investment Banker | 800,000 – 1,200,000 |
| Risk Manager | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Finance Manager | 800,000 – 1,300,000 |
| Auditor | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Credit Analyst | 450,000 – 700,000 |
| Treasury Manager | 600,000 – 1,000,000 |
| Financial Planner | 500,000 – 850,000 |
Sweden's focus on quality education makes it attractive to teachers, especially those in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and special education.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Primary School Teacher | 350,000 – 450,000 |
| Secondary School Teacher | 450,000 – 600,000 |
| ESL Teacher | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Special Education Teacher | 500,000 – 700,000 |
| University Lecturer | 700,000 – 1,000,000 |
| Academic Advisor | 600,000 – 800,000 |
| School Administrator | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Curriculum Developer | 500,000 – 800,000 |
| Vocational Trainer | 450,000 – 650,000 |
| Education Consultant | 700,000 – 1,000,000 |
Sweden’s workforce demand is shaped by key demographic and economic factors. Understanding these trends can help job seekers and employers align with areas of national priority:
As of recently, approximately 20% of Sweden’s population is aged 65 and over. This is driving strong demand for healthcare professionals, eldercare workers, and medical support staff to meet the growing needs of an ageing society.
Sweden’s rapid adoption of AI, automation, and data-led technologies is fuelling the need for skilled professionals in software development, cybersecurity, data science, and IT infrastructure.
There is an ongoing skills gap in trades and vocational sectors. Employers across construction, logistics, transportation, and skilled trades continue to report difficulty hiring trained professionals, particularly in roles such as electricians, plumbers, and machine operators.
Sweden offers multiple work visa options for UK Professionals. Some of the popular Swedish work visa options are given below.

A work permit in Sweden allows non-EU, EEA, or Swiss citizens to gain legal employment. Such a permit is generally required when a Swedish company offers a job to someone from outside these regions. The initial permit is typically valid for two years and is subject to renewal.
The EU Blue Card simplifies employment for skilled workers in Sweden. This program provides non-EU citizens with a legal avenue to reside and work in Sweden for a duration of two years, given they possess a job offer from a Swedish company. The Blue Card also extends certain relocation assistance to family members and eases the process of moving to other EU countries.
The Sweden Job Seeker Visa permits non-EU/EEA individuals to enter Sweden for 3 to 9 months to seek work. This visa serves skilled workers interested in exploring job opportunities within Sweden. Should they secure employment during the visa's validity, they can apply for a standard work permit to remain in the country.
The Swedish Intra-Company Transfer visa lets people from outside the EU/EEA and Switzerland work temporarily in Sweden. They must be employed by a company not in the EU/EEA but need to move to a related business—like a subsidiary—in Sweden. This visa is for managers, specialists, or trainees and helps global companies with short-term assignments.
The Sweden freelance visa, known formally as a residence permit for self-employed individuals, allows non-EU/EEA citizens to reside and work in Sweden as freelancers. This permit is intended for individuals planning to start a business, manage a business, or acquire part ownership in a company for a period exceeding three months.
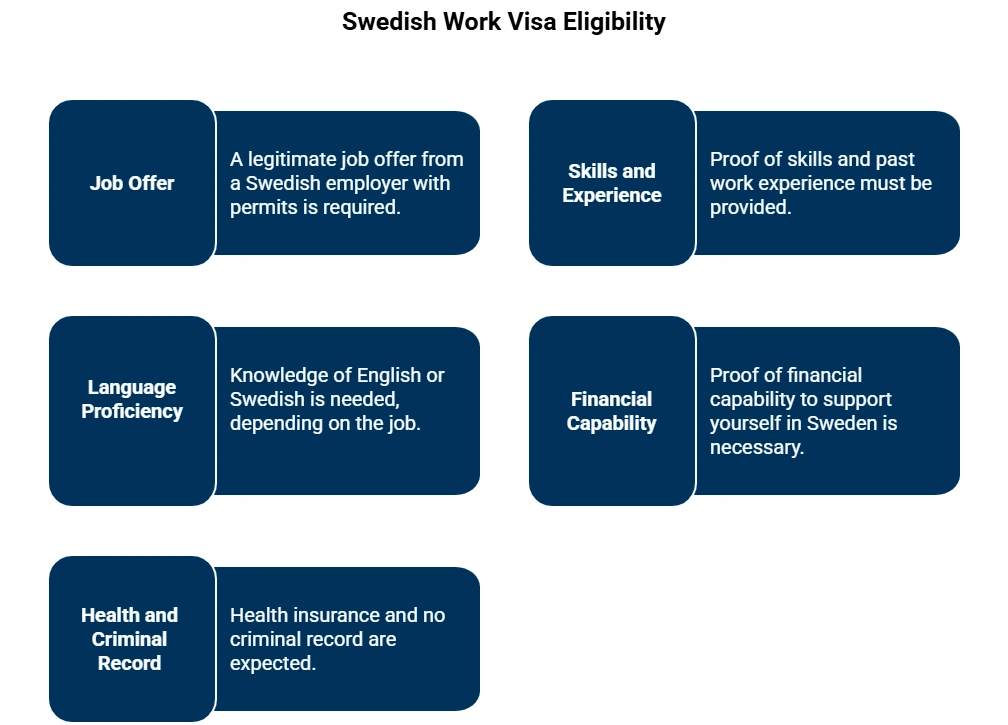
To be eligible for a Swedish Work Visa, you must meet the eligibility criteria given below.
To apply for a Sweden Work Visa, applicants must provide the following documents:
To apply for a Swedish work visa, adhere to the steps below:
Step 1: Secure a formal job offer from a company located in Sweden.
Step 2: Gather all mandatory documents, which might include your resume, certificates, and health records.
Step 3: Submit your visa application through the Swedish Migration Agency or have your employer do it.
Step 4: Pay the work visa application fee.
Step 5: Once your work visa is approved, you can reside and work in Sweden.
.webp)
Detailed information about the processing times for different types of Swedish work visa are given below.
| Visa Type | Processing Time |
| Sweden Work Permit | 2 to 3 months |
| EU Blue Card | 1 to 2 months |
| Job Seeker Visa | 4 to 6 weeks |
| Intra-Company Transfer Visa | 2 to 3 months |
| Freelance Visa | 1 to 3 months |
Detailed information about the application costs of Sweden Work Visas is given below.
| Visa Type | Application Fee (SEK) |
| Sweden Work Permit | SEK 2,200 |
| EU Blue Card | SEK 2,200 |
| Job Seeker Visa | SEK 2,000 |
| Intra-Company Transfer Visa | SEK 2,200 |
| Freelance Visa | SEK 2,500 |
You can follow the below steps to find and apply for jobs in Sweden:
Step 1: Identify roles from the official shortage occupation list (via Arbetsförmedlingen or EURES)
Step 2: Check eligibility and qualifications for your field
Step 3: Secure a job offer from a Sweden-registered employer
Step 4: Apply for a work permit via Migrationsverket (Swedish Migration Agency)
Step 5: Upon arrival, register with Skatteverket for a personal number
Step 6: Start working and apply for family reunification if applicable
Working in Sweden provides several advantages:
Y-Axis, with over 25 years of experience, offers immigration advice in the UK. We offer help with:
Explore what Global Citizens have to say about Y-Axis in shaping their future
Australia PR Visa
One of our client Varun Mathur has opted
Read More...
Australia PR Visa
Uday Seshadri giving feedback after rece
Read More...
Australia PR Visa
Y-Axis received a great feedback from Su
Read More...
Sweden has a strong demand for skilled professionals from the UK in several key sectors. There are many open positions in information technology for software developers and data scientists. The engineering sector also needs people, particularly civil, mechanical, and electrical engineers. Healthcare has openings for doctors, nurses, and physiotherapists. The finance field seeks financial analysts and accountants to fill available jobs. Lastly, electricians and plumbers are wanted to help with the country’s infrastructure projects.
Sweden offers various options for international individuals. Some of the popular Swedish work visas are given below.
| Visa Type | Description | Duration |
| Sweden Work Permit | Non-EU citizens need a work permit after securing a job offer. The permit is typically valid for two years and can be extended. | 2 years (extendable) |
| EU Blue Card | For skilled workers from outside the EU. Allows you to live and work in Sweden and other EU countries with a qualifying job offer. | Valid as per job offer |
| Job Seeker Visa | Allows non-EU citizens to enter Sweden and look for work for up to six months. Proof of sufficient funds is required. | Up to 6 months |
| Intra-Company Transfer Visa | Allows workers from global companies to temporarily move to Sweden for short-term assignments within the same company. | Up to 1 year (extendable) |
| Freelance Visa | For self-employed professionals. Requires proof of self-sufficiency and business contracts. | Varies based on contract |
UK professionals looking for work in Sweden should be aware of the following qualifications:
The process to apply for a Sweden Work Visa is given below.
Step 1: Get a job offer from a Swedish company.
Step 2: Have your employer provide a Certificate of Employment for your visa application.
Step 3: Collect the necessary documents, including proof of your qualifications, evidence of financial stability, and your passport.
Step 4: Send your visa application and documents to the Swedish government.
Step 5: After your visa is approved, you can enter Sweden and begin your job.
The processing time for Sweden work visas are given below.
| Visa Type | Processing Time |
| Sweden Work Permit | 2 to 3 months |
| EU Blue Card | 1 to 2 months |
| Job Seeker Visa | 4 to 6 weeks |
| Intra-Company Transfer Visa | 2 to 3 months |
| Freelance Visa | 1 to 3 months |
The application cost for a Swedish work visa differs based on the visa type. Here are the application prices for some Swedish work visas.
| Visa Type | Application Fee (SEK) |
| Sweden Work Permit | SEK 2,200 |
| EU Blue Card | SEK 2,200 |
| Job Seeker Visa | SEK 2,000 |
| Intra-Company Transfer Visa | SEK 2,200 |
| Freelance Visa | SEK 2,500 |
In Sweden, while Swedish is the official language, many companies, especially those in IT, finance, and engineering, use English as their main language. To roles that require contact with the Swedish public or specific professional licenses, such as those in healthcare, you may have to know Swedish, usually at the B2 level. It's a good idea to learn some basic Swedish to make your career options better and fit into Swedish society more easily.
The benefits of working in Sweden are given below.
The salary expectations of IT professionals in Sweden are given below.
| Job Role | Average Annual Salary (SEK) |
| Software Developer | 500,000 – 700,000 |
| Data Scientist | 600,000 – 800,000 |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | 600,000 – 1,000,000 |
| IT Project Manager | 700,000 – 1,100,000 |
| Cloud Engineer | 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Network Administrator | 400,000 – 600,000 |
| Systems Analyst | 500,000 – 800,000 |
| IT Consultant | 600,000 – 950,000 |
| DevOps Engineer | 600,000 – 850,000 |
| Web Developer | 450,000 – 700,000 |
Yes, Sweden presents numerous opportunities for career progress, notably in the IT, engineering, and healthcare fields. The nation's emphasis on innovation, digital change, and sustainability produces a lively job market for qualified workers. A lot of companies support ongoing education, provide growth programs, and value work-life balance, which helps with career growth over time. Permanent residency options also improve job security and career chances in Sweden.
As of 2025, Sweden faces critical labour shortages across several key sectors. According to official sources, approximately 189 occupations are currently in demand, including:
Additionally, Statistics Sweden reported a deficit of around 70,000 workers, including shortages of 1,100 primary teachers and 400 special needs educators. These roles are prioritised under Sweden’s work permit and labour migration policies.
Yes, proficiency in Swedish is mandatory for most healthcare and education professions. Regulated roles, which include nurses, doctors, psychologists, and teachers require official licensing through bodies such as Socialstyrelsen or educational authorities. Licensing typically involves demonstrating language competency, often at B2 level, along with credential recognition and sometimes practical assessments. While temporary roles or assistant positions may be more flexible, fluency in Swedish is essential for effective patient or student communication and professional integration.
As of June 17, 2025, Sweden requires foreign workers to earn a minimum of SEK 29,680 per month, which represents 80% of the updated median salary (SEK 37,100). Applicants submitting a work permit are subject to this standard unless exempt (e.g., EU/EEA nationals, seasonal workers, EU Blue Card applicants). This ensures fair compensation and safeguards the Swedish labor market against wage undercutting. Applications submitted before this date may still be assessed against the previous median threshold.
Yes, special needs teachers and vocational educators are among the professions facing acute shortages. Statistics Sweden reports a deficit of around 400 special teachers in just the third quarter of 2024. On top of this, vocational educators particularly those teaching trades and technical subjects—are consistently listed among academic and training roles in short supply, highlighting strong opportunities for qualified educators.
The Swedish Council for Higher Education (UHR) oversees the recognition process for foreign credentials. Using their Qualifications Assessment Tool, applicants can determine how their degree compares to Swedish standards and download a certificate validating equivalence. Recognition enables employers or institutions to understand your educational level, and it is often a prerequisite for regulated professions. The process is free of charge and supports both job seekers and students in gaining clarity about their qualifications.